Sliding Window Approach Explained
Sliding window approach can be effective technique to use for certain set of problems. Sliding window technique usually helps us to reduce the time complexity from to
. We create a sliding window which slides through input array.
There are two types of sliding window,
- Fixed size sliding window
- Flexible size sliding window
On the right side, elements are added and on the left side, elements are removed.
Fixed Size Sliding Window
In this type, the size of the sliding window is given in the questing itself.
Question: Maximum Sum Subarray of Size K.
Example 1:
Input: [2, 1, 5, 1, 3, 2], k=3 Output: 9 Explanation: Subarray with maximum sum is [5, 1, 3].
Example 2:
Input: [2, 3, 4, 1, 5], k=2 Output: 7 Explanation: Subarray with maximum sum is [3, 4].
We have to find a subarray of size k with maximum sum Here size of the sliding window is k. At each step, the element on the right side is added to the sum and the element on the left side is subtracted from the sum. We compare the current sum with the max sum in each step. 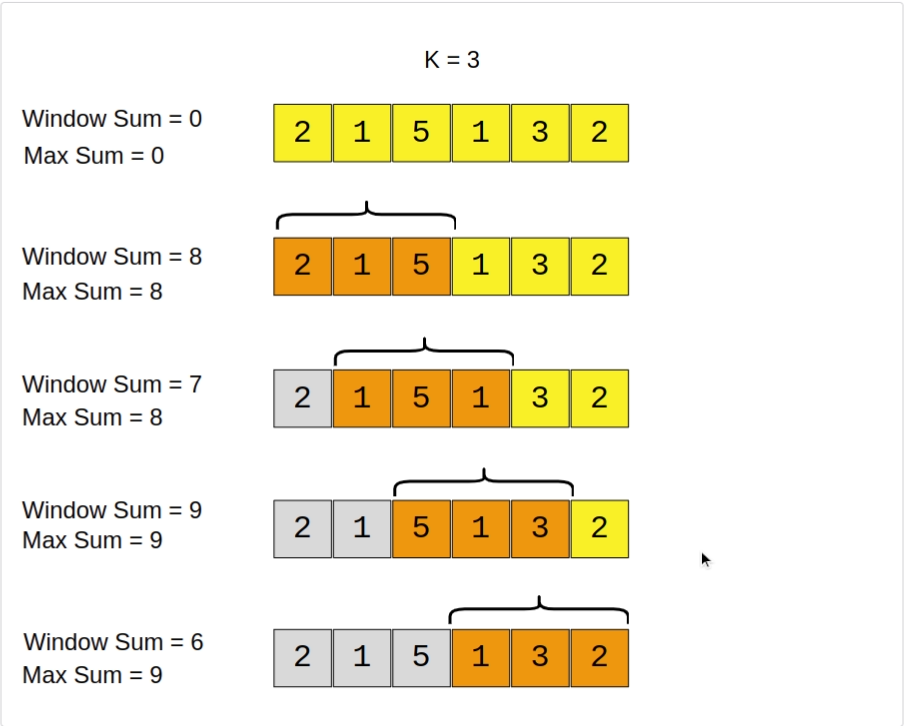
Program:
public int findMaxKSizeSubArray(int[] nums)
{
int max =0,sum=0;
for(int start = 0; end= 0; end<nums.length; end++)
{
sum+=nums[end]; // add next element
if(end>=k-1) // remove elements from start only if window size reached k
{
sum -= nums[start]; //subtract element going out
sum = Math.max(max,sum);
start ++;
}
}
return max;
}
Flexible Size Sliding Window
In this type, the sliding window size is dynamic. We increase/decrease the sliding window based on certain conditions.
Question: Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters. Given the string, find the longest substring which contains only distinct characters.
Example 1:
Input: s = "abcabb" Output: 3 Explanation: The ansnwer is "abc", with the length of 3.
Example 2:
Input: s = "bbbbb" Output: 1 Explanation: The answer is "b", with the length of 1.
This is an example of a dynamic size sliding window. The only condition is that all the characters inside the window must be distinct. We can use a HashMap to remember the last seen index of each character we have processed. Here is how we will solve this problem:
- We keep adding elements to the window until the window contains only distinct characters.
- On each step keep updating the character and their lastSeenIndex in the HashMap.
- If the character added to the right side is already present in the HashMap, then move the start pointer to a particular character’s lastSeenIndex + 1. After this, the window will contain will only distinct characters.
- The longest sliding window with distinct characters is the longest substring without repeating characters.
Program:
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
//Size not fixed. window increase till we have distinct characters.
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
int max = 0;
Map<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int st = 0;
for(int en = 0; en<arr.length; en++)
{
//Increase st only if the map.get(arr[en]) have position more than current st. Ex: abba In this when we reach second a, current st =2 but map.get(en) = 0. So no need to change st.
if(map.containsKey(arr[en]) && st <= map.get(arr[en]))
{
st = map.get(arr[en])+1;
}
map.put(arr[en],en); //store last seen index
int windowSize = en-st+1;
max = Math.max(max,windowSize);
}
return max;
}
Other Sliding Window Posts:
Minimum Size Subarray Sum | Sliding Window
Practice Problems:

