Climbing Stairs Interview Question
This is climbing Stairs Interview question. You are climbing a staircase. It takes n steps to reach the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Example 1:
Input: n = 2 Output: 2 Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top. 1. 1 step + 1 step 2. 2 steps
Example 2:
Input: n = 3 Output: 3 Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top. 1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step 2. 1 step + 2 steps 3. 2 steps + 1 step
Approach:
Lets first start with small input. If No. of steps = 2, then we can reach step 2 in two ways. 1 step from previous step or directly taking 2 steps.
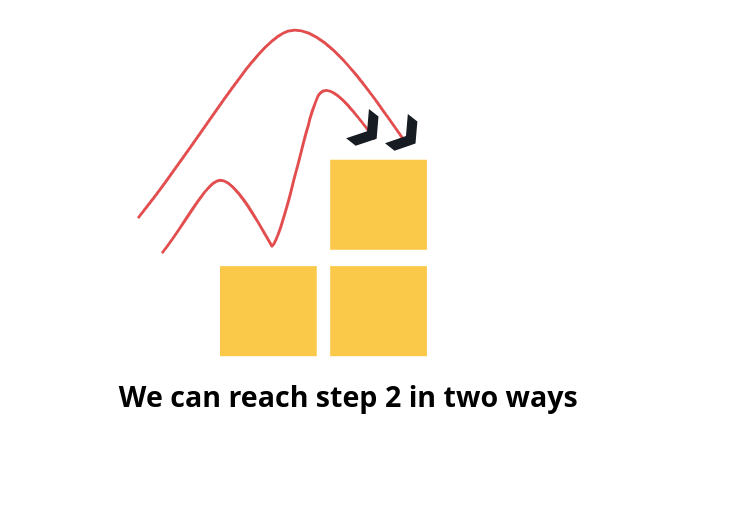
i = 2 combinations are
“1 1”
“2”
We know the to reach the ith point we can take 1 step from i-1 point or 2 steps form i-2 point. So,
No.of ways to reach i = No.of.ways to reach i-1 + No.of.ways to reach i -2
Example: i = 3
We can make 1 step from Combinations of i-1 ,
” 1 1″ | ” 1 ”
” 2 ” | ” 1″
We can make 2 step from Combinations of i-2
” 1 ” | ” 2 ”
So Total Combinations = 2 + 1 = 3
To solve this we have to store the no.of ways to reach/climb each step. We can use bottom up approach. Check out another problem solved using bottom up approach. Bottom up approach( also known as Dynamic Programming ) means we first solve all the sub-problems and combine all the result of sub problem to find answer for original problem.
We store the subproblem result in dp array. dp[i] will contain the no.of.ways to reach ith position.
Program:
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n == 1)
return 1;
int dp[] = new int[n+1];
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = 2;
for(int i = 3; i<=n; i++)
{
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2];
}
return dp[n];
}
}
Analysis:
Time Complexity – O(n) since we traverse the input array once.
Space Complexity – O(n) since we store the subproblem results in dp array
Another Approach:
Can we optimize it further? Yes. At each position we need only previous two results. We might not need dp array. I will leave the implementation to you. Hint: Fibonacci

