Set Operation Program Using C++
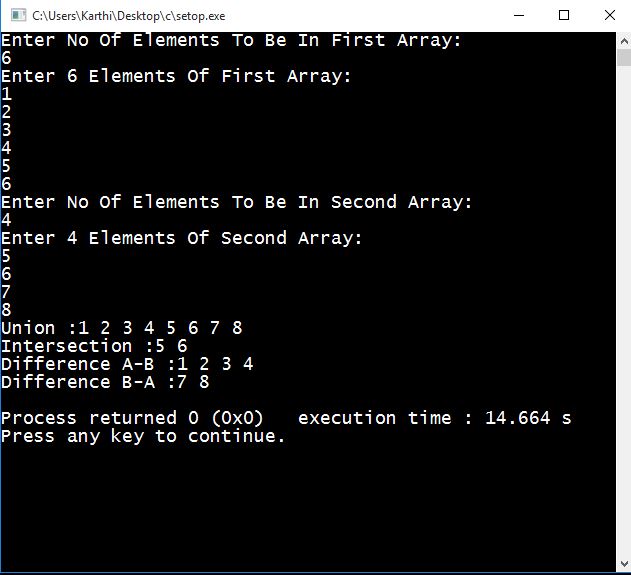
Set Operation Program:
Write set operation program. To perform set operation using C++
EXPLANATION:
Union
Union of the sets A and B, denoted by A ∪ B, is the set of distinct element belongs to set A or set B, or both.
Above is the Venn Diagram of A U B.
Example : Find the union of A = {2, 3, 4} and B = {3, 4, 5};
Solution : A ∪ B = {2, 3, 4, 5}.
Intersection
The intersection of the sets A and B, denoted by A ∩ B, is the set of elements belongs to both A and B i.e. set of the common element in A and B.
Above is the Venn Diagram of A ∩ B.
Example: Consider the previous sets A and B. Find out A ∩ B.
Solution : A ∩ B = {3, 4}.
Set Difference
Difference between sets is denoted by ‘A – B’, is the set containing elements of set A but not in B. i.e all elements of A except the element of B.
Above is the Venn Diagram of A-B.
OUTPUT SCREEN:
/*
* Program for Set Operations
* Author : Karthi Thangavel
* Revised Date : 12/12/2019
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
class SetOperations
{
public:
void setUnion(int *firstArray,int firstArraySize,int *secondArray,int secondArraySize);
void setIntersection(int *firstArray,int firstArraySize,int *secondArray,int secondArraySize);
void setDifference(int *firstArray,int firstArraySize,int *secondArray,int secondArraySize);
void setDisplay(int *resultArray,int resultArraySize);
};
int main()
{
int firstArray[10];int secondArray[10];
int firstArraySize;int secondArraySize;
int i,j,flag=0;// Loop controls
//This part allow the user to store first array elements
cout<<"Enter No Of Elements To Be In First Array:\n";
cin>>firstArraySize;
cout<<"Enter "<<firstArraySize<<" Elements Of First Array:\n";
for(i=0;i<firstArraySize;i++)
{
cin>>firstArray[i];
}
//This part allow the user to store second array elements
cout<<"Enter No Of Elements To Be In Second Array:\n";
cin>>secondArraySize;
cout<<"Enter "<<secondArraySize<<" Elements Of Second Array:\n";
for(i=0;i<secondArraySize;i++)
{
cin>>secondArray[i];
}
//Object for Set Class
SetOperations s;
//Calling the SetOperations Class member function through the object
cout<<"Union :";
s.setUnion(firstArray,firstArraySize,secondArray,secondArraySize);
cout<<"Intersection :";
s.setIntersection(firstArray,firstArraySize,secondArray,secondArraySize);
cout<<"Difference A-B :";
s.setDifference(firstArray,firstArraySize,secondArray,secondArraySize);
cout<<"Difference B-A :";
s.setDifference(secondArray,secondArraySize,firstArray,firstArraySize);
return 0;
}
void SetOperations::setDisplay(int *resultArray,int resultArraySize)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<resultArraySize;i++)
{
cout<<resultArray[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
} //setDisplay method allows to display the final result to the output screen.
void SetOperations::setUnion(int *firstArray,int firstArraySize,int *secondArray,int secondArraySize)
{
int i,j,flag=0,resultArray[20],resultArraySize=0;
for(i=0;i<firstArraySize;i++)
{
resultArray[i]=firstArray[i];
resultArraySize++;
}// Copy the first array elements to result array.
for(i=0;i<secondArraySize;i++)
{
flag=0;
for(j=0;j<resultArraySize;j++)
{
if(secondArray[i]==resultArray[j])
{
flag=1;
break;
}
} // Toggle a flag, if second array element match with result array element.
if(flag==0)
{
resultArray[resultArraySize]=secondArray[i];
resultArraySize++;
} //Copy the second array elements to result array, if condition is true.
}
setDisplay(resultArray,resultArraySize);
}
//
void SetOperations::setIntersection(int *firstArray,int firstArraySize,int *secondArray,int secondArraySize)
{
int i,j,flag=0,resultArray[20],resultArraySize=0;
for(i=0;i<secondArraySize;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<firstArraySize;j++)
{
if(secondArray[i]==firstArray[j])
{
resultArray[resultArraySize]=secondArray[i];
resultArraySize++;
break;
}
}
} // Compare second array elements to first array elements
// Copy the matched elements to result Array.
setDisplay(resultArray,resultArraySize);
}
//
void SetOperations::setDifference(int *firstArray,int firstArraySize,int *secondArray,int secondArraySize)
{
int i,j,flag=0,resultArray[20],resultArraySize=0;
for(i=0;i<firstArraySize;i++)
{
flag=0;
for(j=0;j<secondArraySize;j++)
{
if(firstArray[i]==secondArray[j])
{
flag=1;
break;
}
} // Toggle a flag, if second array element match with result array element.
if(flag==0)
{
resultArray[resultArraySize]=firstArray[i];
resultArraySize++;
}
} //Copy the second array elements to result array, if condition is true.
setDisplay(resultArray,resultArraySize);
}




